Page 18 - Biodiversity and Conservation Framework
P. 18
Biodiversity & Conservation Framework
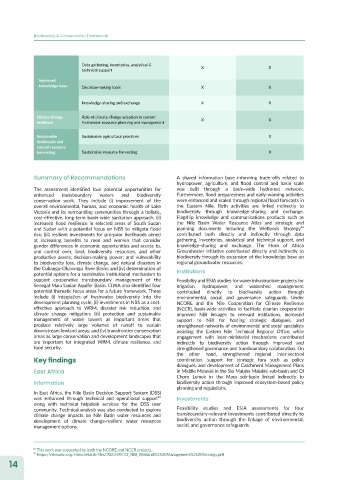
Data gathering, inventories, analytical & X X
technical support
Improved
knowledge base Decision-making tools X X
knowledge-sharing and exchange X X
Climate change Role of climate change adaption in current X X
resilience freshwater resource planning and management
Sustainable Sustainable agricultural practices X
livelihoods and
natural resource
harvesting Sustainable resource harvesting X
Summary of Recommendations A shared information base informing trade-offs related to
hydropower, agriculture, and flood control and basin scale
The assessment identified four potential opportunities for was built through a basin-wide hydromet network.
enhanced transboundary waters and biodiversity Furthermore, flood preparedness and early-warning activities
conservation work. They include (i) improvement of the were enhanced and scaled through regional flood forecasts in
overall environmental, human, and economic health of Lake the Eastern Nile. Both activities are linked indirectly to
Victoria and its surrounding communities through a holistic, biodiversity through knowledge-sharing and exchange.
cost-effective, long-term basin-wide sanitation approach; (ii) Flagship knowledge and communications products such as
increased flood resilience in selected areas of South Sudan the Nile Basin Water Resource Atlas and strategic and
and Sudan with a potential focus on NBS to mitigate flood planning documents including the Wetlands Strategy²⁶
risk; (iii) resilient investments for pro-poor livelihoods aimed contributed both directly and indirectly through data
at increasing benefits to men and women that consider gathering, inventories, analytical and technical support, and
gender differences in economic opportunities and access to, knowledge-sharing and exchange. The Horn of Africa
and control over, land, biodiversity resources, and other Groundwater Initiative contributed directly and indirectly to
productive assets; decision-making power; and vulnerability biodiversity through its expansion of the knowledge base on
to biodiversity loss, climate change, and natural disasters in regional groundwater resources.
the Cubango-Okavango River Basin; and (iv) determination of Institutions
potential options for a sustainable institutional mechanism to
support cooperative transboundary management of the Feasibility and ESIA studies for water infrastructure projects for
Senegal-Mauritanian Aquifer Basin. CIWA also identified four irrigation, hydropower, and watershed management
potential thematic focus areas for a future framework. These contributed directly to biodiversity action through
include (i) integration of freshwater biodiversity into the environmental, social, and governance safeguards. Under
development planning cycle; (ii) investments in NBS as a cost- NCORE and the Nile Cooperation for Climate Resilience
effective approach to WRM, disaster risk reduction, and (NCCR), basin-wide activities to facilitate riparian cooperation
climate change mitigation; (iii) protection and sustainable improved NBI linkages to relevant institutions, increased
management of water towers as important areas that support to NBI for hosting strategic dialogues, and
produce relatively large volumes of runoff to sustain strengthened networks of environmental and social specialists
downstream lowland areas; and (iv) transfrontier conservation assisting the Eastern Nile Technical Regional Office, while
areas as large conservation and development landscapes that engagement with inter-ministerial mechanisms contributed
are important for integrated WRM, climate resilience, and indirectly to biodiversity action through improved and
food security. strengthened governance and transboundary collaboration. On
the other hand, strengthened regional inter-sectoral
Key findings coordination, support for strategic fora such as policy
dialogues, and development of Catchment Management Plans
East Africa in Middle Malakisi in the Sio Malaba Malakisi sub-basin and Ol
Choro Lemek in the Mara sub-basin linked indirectly to
Information biodiversity action through improved ecosystem-based policy
planning and regulations.
In East Africa, the Nile Basin Decision Support System (DSS)
was enhanced through technical and operational support²⁵ Investments
along with technical helpdesk services for the DSS user
community. Technical analysis was also conducted to explore Feasibility studies and ESIA assessments for four
climate change impacts on Nile Basin water resources and transboundary-relevant investments contributed directly to
development of climate change-resilient water resources biodiversity action through the linkage of environmental,
management options. social, and governance safeguards.
²⁵ This work was supported by both the NCORE and NCCR projects.
²⁶ https://nilebasin.org/sites/default/files/2023-09/43_NBI_Wetland%2520Management%2520Strategy.pdf
14