Page 24 - CIWA’s FCV Framework
P. 24
Case Study – Kariba Dam Rehabilitation Project
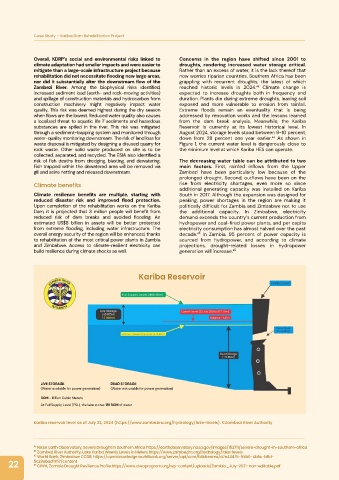
Overall, KDRP’s social and environmental risks linked to Concerns in the region have shifted since 2001 to
climate adaptation had smaller impacts and were easier to droughts, rendering increased water storage critical.
mitigate than a large-scale infrastructure project because Rather than an excess of water, it is the lack thereof that
rehabilitation did not necessitate flooding new large areas, now worries riparian countries. Southern Africa has been
nor did it substantially alter the downstream flow of the grappling with recurrent droughts, the latest of which
Zambezi River. Among the biophysical risks identified, reached historic levels in 2024.⁴³ Climate change is
increased sediment load (earth- and rock-moving activities) expected to increase droughts both in frequency and
and spillage of construction materials and hydrocarbon from duration. Plants die during extreme droughts, leaving soil
construction machinery might negatively impact water exposed and more vulnerable to erosion from rainfall.
quality. This risk was deemed highest during the dry season Extreme floods remain an eventuality that is being
when flows are the lowest. Reduced water quality also causes addressed by renovation works and the lessons learned
a localized threat to aquatic life if sediments and hazardous from the dam break analysis. Meanwhile, the Kariba
substances are spilled in the river. This risk was mitigated Reservoir is currently at its lowest historical level. In
through a sediment-trapping system and monitored through August 2024, storage levels stood between 9-10 percent,
water-quality monitoring downstream. The risk of land loss for down from 28 percent one year earlier.⁴⁴ As shown in
waste disposal is mitigated by designing a disused quarry for Figure 1, the current water level is dangerously close to
rock waste. Other solid waste produced on site is to be the minimum level at which Kariba HES can operate.
collected, separated, and recycled. The ESIA also identified a
risk of fish deaths from dredging, blasting, and dewatering. The decreasing water table can be attributed to two
Fish trapped within the dewatered area will be removed via main factors. First, rainfed inflows from the Upper
gill and seine netting and released downstream. Zambezi have been particularly low because of the
prolonged drought. Second, outflows have been on the
Climate benefits rise from electricity shortages, even more so since
additional generating capacity was installed on Kariba
Climate resilience benefits are multiple, starting with South in 2017. Although the expansion was designed for
reduced disaster risk and improved flood protection. peaking, power shortages in the region are making it
Upon completion of the rehabilitation works on the Kariba politically difficult for Zambia and Zimbabwe not to use
Dam, it is projected that 3 million people will benefit from the additional capacity. In Zimbabwe, electricity
reduced risk of dam breaks and avoided flooding. An demand exceeds the country’s current production from
estimated US$8 billion in assets will be better protected hydropower and coal-fired power plants, and per capita
from extreme flooding, including water infrastructure. The electricity consumption has almost halved over the past
overall energy security of the region will be enhanced, thanks decade.⁴⁵ In Zambia, 95 percent of power capacity is
to rehabilitation of the most critical power plants in Zambia sourced from hydropower, and according to climate
and Zimbabwe. Access to climate-resilient electricity can projections, drought-related losses in hydropower
build resilience during climate shocks as well. generation will increase.⁴⁶
Kariba Reservoir
LIVE STORAGE DEAD STORAGE
(Water available for power generation) (Water not usable for power generation)
BCM - Billion Cubic Meters
At Full Supply Level (FSL), the lake stores 181 BCM of water
Kariba reservoir level as of July 22, 2024 (https://www.zambezira.org/hydrology/lake-levels). ©Zambezi River Authority
⁴³ NASA Earth Observatory, Severe Drought in Southern Africa https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/images/152711/severe-drought-in-southern-africa
⁴⁴ Zambezi River Authority, Lake Kariba Weekly Levels in Meters https://www.zambezira.org/hydrology/lake-levels
⁴⁵ World Bank, Zimbabwe CCDR, https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/a7e43475-55b0-4b6c-bfb1-
22 5c23ebad1957/content
⁴⁶ CIWA, Zambia Drought Resilience Profile https://www.ciwaprogram.org/wp-content/uploads/Zambia_July-2021-non-editable.pdf