Page 23 - CIWA’s FCV Framework
P. 23
Case Study – Kariba Dam Rehabilitation Project
CIWA’s influence
From its inception in 2011, CIWA selected the Zambezi Program and the two recipient-executed Zambezi River
as one of its priority basins of engagement. CIWA rolled Development and Zambezi River Management projects.
out a series of three grants as part of its ZRB programmatic Table 8 provides an overview of CIWA’s programmatic
approach: the Bank-executed Zambezi River Basin Support approach in the ZRB.
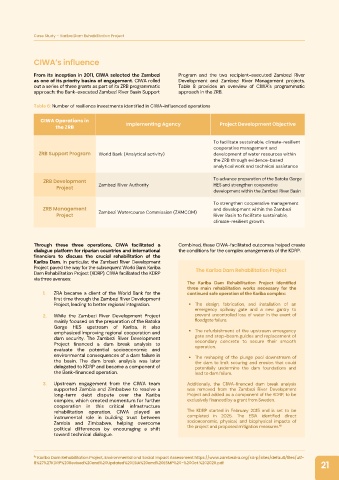
Table 6: Number of resilience investments identified in CIWA-influenced operations
CIWA Operations in
the ZRB Implementing Agency Project Development Objective
To facilitate sustainable, climate-resilient
cooperative management and
ZRB Support Program World Bank (Analytical activity) development of water resources within
the ZRB through evidence-based
analytical work and technical assistance
ZRB Development To advance preparation of the Batoka Gorge
Project Zambezi River Authority HES and strengthen cooperative
development within the Zambezi River Basin
To strengthen cooperative management
ZRB Management and development within the Zambezi
Project Zambezi Watercourse Commission (ZAMCOM) River Basin to facilitate sustainable,
climate-resilient growth.
Through these three operations, CIWA facilitated a Combined, these CIWA-facilitated outcomes helped create
dialogue platform for riparian countries and international the conditions for the complex arrangements of the KDRP.
financiers to discuss the crucial rehabilitation of the
Kariba Dam. In particular, the Zambezi River Development
Project paved the way for the subsequent World Bank Kariba The Kariba Dam Rehabilitation Project
Dam Rehabilitation Project (KDRP). CIWA facilitated the KDRP
via three avenues:
The Kariba Dam Rehabilitation Project identified
three main rehabilitation works necessary for the
1. ZRA became a client of the World Bank for the continued safe operation of the Kariba complex:
first time through the Zambezi River Development
Project, leading to better regional integration. The design, fabrication, and installation of an
emergency spillway gate and a new gantry to
2. While the Zambezi River Development Project prevent uncontrolled loss of water in the event of
mainly focused on the preparation of the Batoka floodgate failure.
Gorge HES upstream of Kariba, it also
emphasized improving regional cooperation and The refurbishment of the upstream emergency
dam security. The Zambezi River Development gate and stop-beam guides and replacement of
Project financed a dam break analysis to secondary concrete to secure their smooth
operation.
evaluate the potential socioeconomic and
environmental consequences of a dam failure in The reshaping of the plunge pool downstream of
the basin. The dam break analysis was later the dam to limit scouring and erosion that could
delegated to KDRP and became a component of potentially undermine the dam foundations and
the Bank-financed operation. lead to dam failure.
3. Upstream engagement from the CIWA team Additionally, the CIWA-financed dam break analysis
supported Zambia and Zimbabwe to resolve a was removed from the Zambezi River Development
long-term debt dispute over the Kariba Project and added as a component of the KDRP, to be
complex, which created momentum for further exclusively financed by a grant from Sweden.
cooperation in this critical infrastructure
rehabilitation operation. CIWA played an The KDRP started in February 2015 and is set to be
instrumental role in building trust between completed in 2025. The ESIA identified direct
Zambia and Zimbabwe, helping overcome socioeconomic, physical, and biophysical impacts of
political differences by encouraging a shift the project and proposed mitigation measures.⁴²
toward technical dialogue.
⁴² Kariba Dam Rehabilitation Project, Environmental and Social Impact Assessment https://www.zambezira.org/kdrp/sites/default/files/utf-
8%27%27KDRP%20Revised%20and%20Updated%20ESIA%20and%20ESMP%20-%20Oct.%202020.pdf 21