Page 63 - CIWA Water Data Revolution Overview Report
P. 63
7.4 Potential for Trainings and Capacity Building on RS Data, Data Platforms, and Analytical
Tools
The potential for utilizing RS data, data platforms and products, and analytical tools using RS to
improve water management practices is evident to the organizations that participated in this
assessment. Sector-wide limitations inhibiting the uptake of conventional, often costly, data tools
and expansive in-situ monitoring networks has led majority of organizations to the conclusion
that RS data and tools are necessary for a long-term sustainable, data-informed decision making
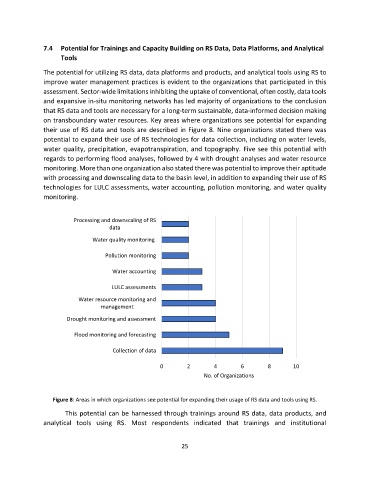
on transboundary water resources. Key areas where organizations see potential for expanding
their use of RS data and tools are described in Figure 8. Nine organizations stated there was
potential to expand their use of RS technologies for data collection, including on water levels,
water quality, precipitation, evapotranspiration, and topography. Five see this potential with
regards to performing flood analyses, followed by 4 with drought analyses and water resource
monitoring. More than one organization also stated there was potential to improve their aptitude
with processing and downscaling data to the basin level, in addition to expanding their use of RS
technologies for LULC assessments, water accounting, pollution monitoring, and water quality
monitoring.
Processing and downscaling of RS
data
Water quality monitoring
Pollution monitoring
Water accounting
LULC assessments
Water resource monitoring and
management
Drought monitoring and assessment
Flood monitoring and forecasting
Collection of data
0 2 4 6 8 10
No. of Organizations
Figure 8: Areas in which organizations see potential for expanding their usage of RS data and tools using RS.
This potential can be harnessed through trainings around RS data, data products, and
analytical tools using RS. Most respondents indicated that trainings and institutional
25