Sur la voie de la relance : comment le Soudan fait repartir son secteur de l'eau (En anglais)
Posté le : 1 octobre 2021 (Blog)

Le Soudan est confronté à une situation difficile mais familière : Comment utiliser des ressources limitées tout en améliorant les moyens de subsistance des populations ?
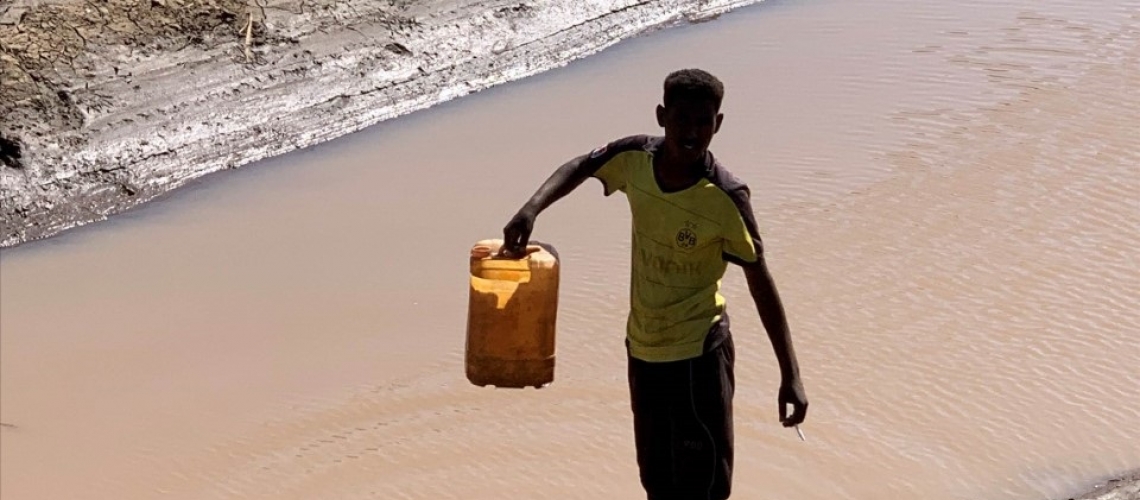
En 2020, alors que le monde lutte contre la pandémie de COVID-19, des inondations dévastatrices frappent le Soudan. Le Nil a atteint son niveau le plus élevé depuis 100 ans, touchant des centaines de milliers de personnes et détruisant des milliers d'habitations.
Ces inondations, et les maladies transmises par l'eau qu'elles entraînent, sont de plus en plus fréquentes au Soudan. En moyenne, les inondations touchent environ 200 000 personnes chaque année : 99 000 en 2017, 222 300 en 2018, 426 300 en 2019 et 875 000 en 2020. Dans le même temps, le pays est confronté à davantage de sécheresses, ce qui accroît la pression sur un système agricole qui subit les conséquences d'un sous-investissement et d'une infrastructure de stockage de l'eau limitée.
La gestion des ressources en eau dans le secteur agricole est particulièrement importante : l'agriculture représente 30 % du PIB du pays et emploie plus de 70 % de la main-d'œuvre. Mais ce secteur est fragile.
Environ 70 % des agriculteurs dépendent de l'agriculture pluviale et la pratiquent collectivement sur 14 millions d'hectares. La sécheresse, le manque d'investissement et l'augmentation de la densité de population ont plongé de nombreux membres de cette communauté dans la pauvreté. Si les niveaux de pauvreté sont relativement faibles dans les systèmes d'irrigation du bassin du Nil, qui couvrent près de 2 millions d'hectares de terres, les systèmes eux-mêmes se sont détériorés en raison de leur inefficacité, du vieillissement des infrastructures, des faibles rendements des cultures et d'une mauvaise gestion. Le changement climatique a exacerbé les défis agricoles du pays, avec une augmentation des inondations et des sécheresses dues à la variabilité des précipitations.
Dans le secteur de l'approvisionnement en eau et de l'assainissement, la prestation de services est semée d'embûches. La taille même du pays pose un énorme défi, tout comme les investissements et la logistique nécessaires pour fournir des services sûrs et abordables. La fonctionnalité globale du système d'approvisionnement en eau du Soudan est d'environ 73 %, selon le "Plan 2019-30 du secteur de l'eau, de l'assainissement et de l'hygiène du Soudan pour la réalisation du sixième objectif de développement durable (SDG6)", qui a été préparé en 2019 par le ministère soudanais de l'irrigation et des ressources en eau et le ministère de la santé, avec le soutien de l'UNICEF.
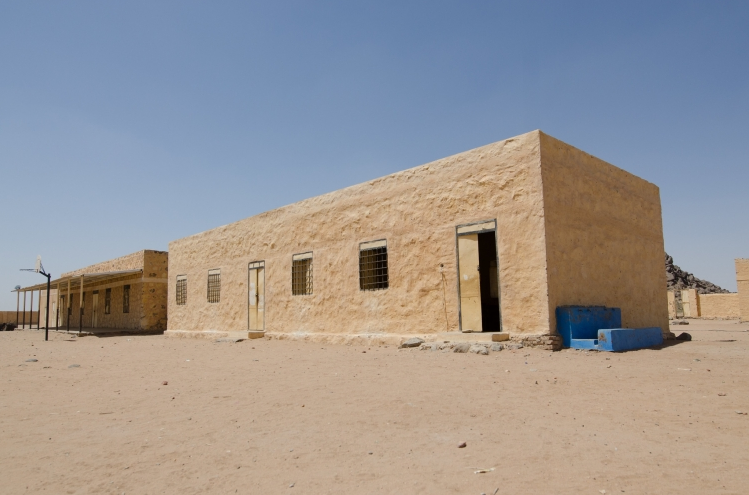

Les améliorations en matière d'approvisionnement et d'assainissement ont été lentes, en particulier dans les zones rurales. Plus de 40 % des ménages soudanais n'ont pas accès à des services d'eau de base, 67 % de la population n'a pas accès à des services d'assainissement de base et 75 % n'a pas accès à des services d'hygiène de base. Cette situation menace gravement la santé et les moyens de subsistance de la population du pays.
Alors que les effets du changement climatique continuent de s'intensifier, le Soudan se trouve à un moment critique de son développement. Le pays s'efforce de renforcer la résilience du secteur de l'eau dans le cadre de ses efforts visant à renouveler le contrat social et à soutenir l'économie.
L'évaluation sectorielle de la Banque mondiale a fourni des solutions concrètes pour permettre au Soudan de relever ses défis en matière d'eau et de devenir plus résilient face aux événements climatiques extrêmes :
- Attirer de meilleurs investissements pour aider le Soudan à financer davantage de projets d'approvisionnement en eau et d'irrigation.
- Améliorer les capacités, la structure et l'efficacité du ministère de l'irrigation et des ressources en eau.
- Effectuer des analyses et des diagnostics plus approfondis des principaux bassins et systèmes d'irrigation.
- Renforcer le développement des capacités du personnel du régime.
- Engager des dépenses dans le secteur public afin d'identifier les domaines à améliorer.
Sur la base de cette évaluation, et reconnaissant le besoin urgent de reconstruire son secteur de l'eau, le Soudan travaille avec l'IDA pour préparer trois projets, axés sur l'amélioration de la gestion intégrée des ressources en eau, y compris les services d'eau et d'assainissement, la revitalisation de l'agriculture irriguée et l'augmentation de la résilience par le biais d'un projet régional dans la Corne de l'Afrique. Il est important de noter que les projets se concentreront également sur le renforcement des capacités de mise en œuvre des projets au sein du ministère de l'irrigation et des ressources en eau.
Le projet axé sur l'agriculture irriguée améliorera l'irrigation, le soutien à l'agriculture et les services de drainage dans des zones sélectionnées au Soudan en établissant des voies pour la mise en place d'institutions robustes pour l'agriculture irriguée, la revitalisation de l'agriculture irriguée et le renforcement des services agricoles.
Les eaux souterraines agissent comme un tampon naturel contre la variabilité du climat, assurant la sécurité dans les pays qui ne disposent pas de services centralisés d'approvisionnement en eau. Le projet régional de la Corne de l'Afrique vise à renforcer la résilience et la sécurité de l'eau dans la région en améliorant la gouvernance des eaux souterraines. Le projet renforcera les connaissances de la région sur les ressources en eaux souterraines disponibles afin de permettre une meilleure gestion coopérative au-delà des frontières des pays. Le Soudan, dont le secteur agricole est mis à rude épreuve et qui est confronté à des problèmes d'approvisionnement en eau et d'assainissement, bénéficiera grandement de l'accès à une ressource en eau bien gérée et facile d'accès.
L'implication de la population du pays dans le renforcement de la résilience de l'eau est une étape importante dans le rétablissement du contrat social et de la confiance entre les citoyens et le gouvernement. Il s'agit là d'un élément central de la réussite du travail du GWSP. Le GWSP travaille avec des partenaires du monde entier pour fournir un soutien opportun et s'assurer que les analyses et les connaissances atteignent les parties prenantes clés d'une manière qui leur convient, qui façonne les discussions et qui influence les politiques et les pratiques.